Storage - Flash Based
Flash Chips are a widely used storage technology. They offer fast read and write speeds. There are three very common flash devices:
- Solid State Drives (SSD)
- USB Flash Memory Sticks
- SD Cards / Micro SD Cards (other flash cards also exist but are not so common)
As well as their fast data transfer speed, their small physical size is a key reason why they became so popular. The fact it can be put into small, portable forms such as an SD card, or a USB Stick, makes it ideal for carrying around data.
Without this, devices such as Smartphones and Digital Cameras would have to have their own internal storage such as a HDD or rely on slow optical media. This would have increased the size of the device and probably limited their popularity.
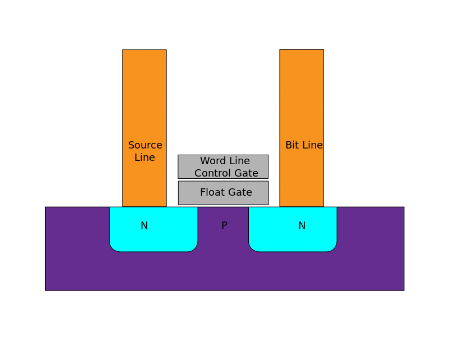
Flash works by using the amount of electrons currently flowing through an "Oxide Layer" (part of the chip) called the "floating gate" to represent binary. If this layer is less than half full then the data is said to be a 0, if it is more than half full it is a 1. This Oxide layer can receive a charge which increases the number of electrons, or it can be drained which decreases them. - See the videos for a bit more on this, or visit howstuffworks.com for a detailed explanation.
Overview of Flash Memory and its uses
Basic explanation of how Flash Memory actually stores data